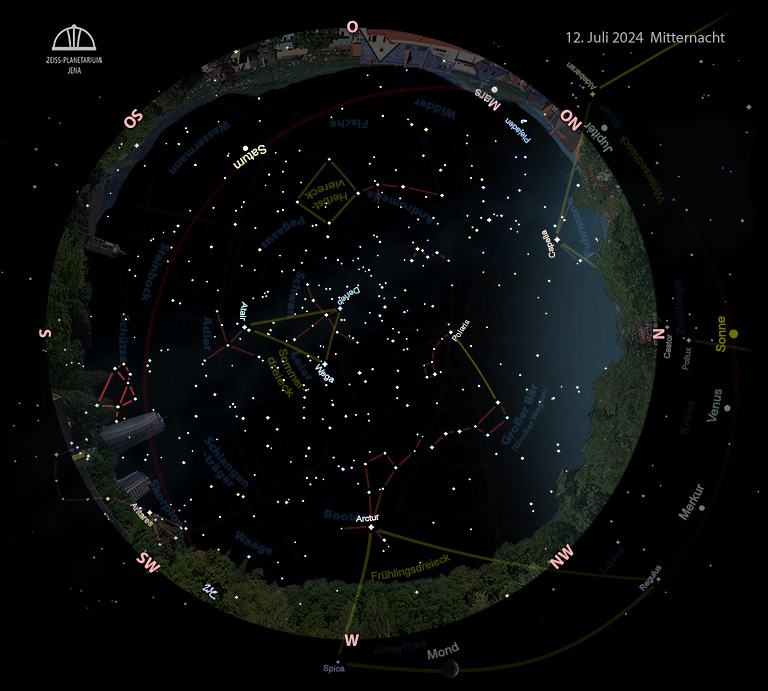
3 Planeten am Morgenhimmel
Unsere Erde erreicht am 5. den sonnenfernsten Punkt ihrer Bahn. Trotzdem herrscht bei uns Hochsommer, der helle Tag ist immer noch länger als 15 Stunden. Die Sonne zieht am 20. Juli vom Tierkreissternbild Zwillinge zum Krebs.
Neumond ist am 6. Juli, Vollmond am 21.
Im Südwesten beginnt sich das Frühlingsdreieck vom Abendhimmel zu verabschieden. Nur der relativ hochstehende Arktur wird noch einige Monate rötlich funkeln. Gegen Mitternacht dominieren hoch im Süden die hellen Sterne des Sommerdreiecks: Deneb, der Schwanzstern im Sternbild Schwan – auch als Kreuz des Nordens bekannt, westlich daneben die Wega in der Leier und Richtung Horizont ist es der Atair im Adler.
Östlich folgen die weniger lichtstarken Sterne des Herbstvierecks, das jedoch durch seine markante Form gut zu entdecken ist und nach und nach den morgendlichen Himmel beherrschen wird.
Um Mitternacht geht Saturn im Osten auf. Er wird zum Planeten der ganzen Nacht. Der rote Nachbarplanet Mars erscheint im Nordosten vor dem Tierkreissternbild Widder, ab 12. vor dem Stier und wird zum Planeten der zweiten Nachthälfte. Jupiter folgt in der Morgendämmerung in östlicher Richtung.
W. Don Eck
Zeiss-Planetarium Jena
The starry sky in July 2024
3 planets in the morning sky
Our Earth reaches the furthest point of its orbit from the Sun on the 5th. However, it is still high summer here and the light day is still longer than 15 hours. The sun moves from Gemini to Cancer on 20 July.
There is a new moon on 6 July and a full moon on 21 July.
In the south-west, the spring triangle begins to recede from the evening sky. Only the relatively high Arcturus will shine reddishly for a few more months. Towards midnight the bright stars of the summer triangle dominate high in the south: Deneb, the tail star in the constellation of Swan – also known as the Northern Cross, next to it to the west is Vega in Lyra, and towards the horizon is Atair in Eagle.
The fainter stars of the Autumnal Quadrilateral follow to the east, but their distinctive shape makes them easy to spot and they will gradually dominate the morning sky.
Saturn rises in the east at midnight. It becomes the planet of the night. Its red neighbour, Mars, appears in the northeast in front of Aries, and from the 12th in front of Taurus, becoming the planet of the second half of the night. Jupiter follows in the east at dawn.