3 Planeten und Zeitumstellung
Die mittägliche Sonnenhöhe verringert sich von 35 Grad bis zum Monatsende auf 25 Grad, damit auch die Länge des hellen Tages auf weniger als 10 Stunden. Am 31. verlässt die Sonne das Tierkreissternbild Jungfrau und zieht vor die Waage.
Am 26. Oktober endet die Mitteleuropäische Sommerzeit 2025 in Deutschland. Die Uhren werden von 3 Uhr auf 2 Uhr zurückgestellt.
Vollmond ist am 7., Neumond am 21. Oktober.
Am frühen Abend ist in östlicher Richtung der Ringplanet Saturn vor dem Tierkreissternbild Wassermann zu sehen. Gegen Mitternacht erscheint im Osten der Riesenplaneten Jupiter vor dem Tierkreissternbild Zwillinge und wird zum Planeten der zweiten Nachthälfte.
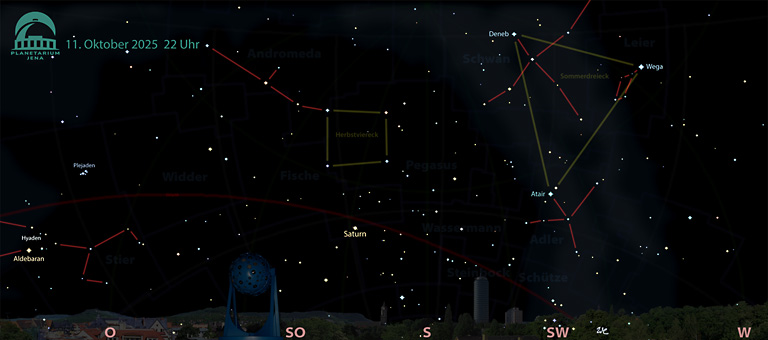
Die frühen Nachtstunden dokumentieren den Abschied vom Sommer, das Sommerdreieck ist bereits im Südwesten zu finden. Der Deneb im Sternbild Schwan, die Wega in der Leier – beide stehen sehr hoch – und der Atair unten bilden dieses gleichschenklige Dreieck. Südlich folgen die weniger hellen Sterne des Herbstvierecks, das aus Sternen der Sternbilder Pegasus und Andromeda besteht. Deren Sternkette weist in den Osten.
In den späteren Nachtstunden bis in den Morgen zeigen sich im Südosten bereits die Sterne des Wintersechsecks. Auffällig sind der Himmelsjäger Orion und der helle funkelnde Sirius im Großen Hund. Im Stier können wir zwei offenen Sternhaufen entdecken, die Plejaden oder Siebengestirn und die Hyaden oder Regengestirn. Der rötliche Aldebaran gehört ebenso zum Wintersechseck wie Kapella hoch darüber, die Zwillinge Kastor und Pollux auf der östlichen Seite sowie Prokyon im Kleinen Hund, Sirius im Großen Hund und Rigel im Orion.
Unser innerer Nachbarplanet Venus ist in der Morgendämmerung am Osthorizont zu finden.
W. Don Eck
Zeiss-Planetarium Jena
The starry sky in October 2025
3 Planets and time changeover
The midday altitude of the sun decreases from 35 degrees to 25 degrees by the end of the month, which means that the length of the light day is also reduced to less than 10 hours. On 31 October, the sun leaves the zodiacal constellation of Virgo and moves in front of Libra.
On 26 October, Central European Summer Time 2025 ends in Germany. The clocks are set back from 3 o’clock to 2 o’clock.
Full moon is on 7 October, new moon on 21 October.
In the early evening, the ringed planet Saturn can be seen in an easterly direction in front of the zodiacal constellation of Aquarius. Around midnight, the giant planet Jupiter appears in the east in front of the zodiacal constellation Gemini and becomes the planet of the second half of the night.
The early hours of the night document the farewell to summer, the summer triangle can already be found in the south-west. Deneb in the constellation Swan, Vega in Lyra – both very high – and Atair below form this isosceles triangle. To the south follow the less bright stars of the autumn quadrilateral, which consists of stars from the constellations Pegasus and Andromeda. Their star chain points to the east.
In the later hours of the night and into the morning, the stars of the winter hexagon can already be seen in the south-east. The sky hunter Orion and the bright, twinkling Sirius in the Great Dog are striking. In Taurus we can discover two open star clusters, the Pleiades or Pleiades and the Hyades or Rainy Stars. The reddish Aldebaran is also part of the winter hexagon, as are Capella high above it, the twins Castor and Pollux on the eastern side and Prokyon in the Little Dog, Sirius in the Big Dog and Rigel in Orion.
Our inner neighbouring planet Venus can be found on the eastern horizon at dawn.